Making the Switch from SSR to SNP: A Game-Changer for Gubba
The agricultural industry has always been driven by innovation and a quest for better ways to cultivate crops and produce superior seeds. In recent years, the industry has witnessed a remarkable transformation as it shifts from traditional genetic markers, such as Simple Sequence Repeats (SSRs), to the more advanced Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) technology. SNP markers have become the gold standard in crop genetic studies, offering remarkable stability, low mutation rates, affordability, and high-throughput genotyping capabilities. This transition marks a pivotal moment in the world of agriculture, where precision and efficiency are paramount. Let’s explore why SNP technology is taking the industry by storm and what it means for the future of agriculture.
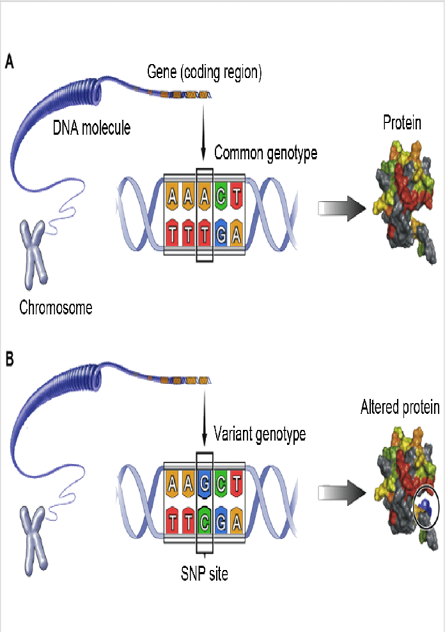
What are SNPs?
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) are stable genetic markers that have gained prominence in recent years. These genetic markers represent single nucleotide variations within DNA sequences. Unlike Simple Sequence Repeats (SSRs), which are composed of repeated sequences of nucleotides, SNPs are the smallest genetic variations, involving only a single base pair change. SNPs are highly prevalent in genomes, making them a valuable resource for genetic analysis.
Why SNP is Better than SSR
When it comes to genetic markers in the field of agriculture, Simple Sequence Repeats (SSRs) have long been a reliable choice. SSRs are known for their high degree of polymorphism, making them an essential tool for crop genetic studies. However, the winds of change are sweeping through the agricultural landscape, and the shift from SSRs to SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) technology is gaining momentum. But what makes SNP superior to SSR, and why is this change necessary, especially when SSR is so popular?
Advanced Technology
SNP technology represents a significant leap forward in the realm of genetic analysis. While SSRs rely on the analysis of repeated sequences of nucleotides, SNPs focus on the smallest genetic variations – single nucleotide changes within DNA sequences. This advanced technology is based on cutting-edge molecular biology and bioinformatics tools, allowing for a more in-depth and precise analysis of genetic data. By leveraging SNP technology, researchers can gain deeper insights into the genetic makeup of crops, paving the way for more targeted and effective breeding programs.
Accurate Results
SNP markers are renowned for their accuracy. Unlike SSRs, which can sometimes produce ambiguous results due to the complexity of repeated sequences, SNPs offer a high degree of reliability. The precise identification of single nucleotide variations provides unambiguous genetic information, reducing the likelihood of misinterpretation or errors in genetic data. This accuracy is invaluable for researchers and seed producers, as it ensures that the decisions they make regarding crop breeding and improvement are based on solid, dependable data.
Faster Results
Time is of the essence in agriculture, and SNP technology excels in this aspect. SNP genotyping not only provides more accurate results but does so in a significantly shorter time frame. In fact, SNP analysis can yield results at least two days earlier than SSR analysis. This time advantage is a game-changer in agriculture, where making swift decisions is often critical. With SNP technology, researchers and seed producers can expedite their breeding programs, ultimately leading to more efficient crop development and improved yields.
Reduced Human Error
SNP technology offers another crucial advantage: it reduces human error. Traditional SSR analysis can be a tedious and labor-intensive process, involving the manual counting and analysis of repeated sequences. This manual aspect of SSR analysis leaves room for human error, which can compromise the quality of the data. SNP technology, on the other hand, relies on software-based analysis, minimizing the potential for human errors. By automating the analysis process, SNP technology ensures consistent and reliable results, regardless of the scale of the study.
In contrast, SSR analysis, though effective, can be a time-consuming and cumbersome task. It involves painstaking manual work to interpret the complex sequences, which not only consumes valuable time but also increases the chances of errors. The transition to SNP technology, with its automated software-driven analysis, not only accelerates the process but also substantially reduces the risk of inaccuracies.
Gubba’s Promise with SNP
Gubba’s decision to switch to SNP technology can open up a world of possibilities for both the company and its clients. With SNP markers, Gubba can offer the following benefits to its clients:
Enhanced Data Quality: SNP markers provide more consistent and accurate data, ensuring that Gubba’s clients have access to reliable genetic information for their crops.
Faster Turnaround: The high-throughput capabilities of SNP genotyping mean that Gubba can process more samples in less time. This translates into faster results for clients, allowing them to make quicker decisions about their breeding programs.
Cost Savings: SNP technology is cost-effective, which can lead to reduced expenses for Gubba and, ultimately, more affordable services for clients.
Improved Crop Performance: By utilising SNP markers to identify genetic loci responsible for desirable traits, Gubba can help its clients in developing improved crop varieties with higher yields, better quality, and resistance to pests and diseases.
Conclusion
The transition from SSR to SNP technology in the agricultural industry is a process that will unfold gradually, ensuring a smooth adaptation for all stakeholders involved. Currently, Gubba has initiated this transformative journey by implementing SNP technology in the analysis of two key crops: tomatoes and paddy. These initial steps serve as a foundation for what promises to be a significant shift in the industry. By starting with these crops, Gubba is not only taking a cautious approach to the transition but also focusing on crops of high economic and agricultural importance. The careful integration of SNP technology into the analysis of these crops allows Gubba to gain valuable insights, optimise their processes, and perfect the application of SNP markers before expanding to other crops. This phased approach demonstrates Gubba’s commitment to maintaining the highest standards of data quality and precision, ensuring that the switch from SSR to SNP is a seamless and beneficial transformation for all.
If you want to explore our SNP services or wish to know more about it, feel free to get in touch with us.
Contact: +91-9121010626
Email: [email protected]


